cable gas pedal
The Interplay of Cable, Gas, and the Pedal A Dive into Automotive Innovation
In the world of automotive engineering, the interaction between components can often dictate a vehicle's performance, handling, and overall driving experience. Among these components, the cable, gas, and pedal form a crucial triad that plays a significant role in the way drivers interact with their vehicles. This article explores the intricate relationship between these elements, how they have evolved over time, and their impact on modern automobiles.
Understanding the Components
At its core, the gas pedal is a simple yet vital interface between the driver and the vehicle's engine. When the driver presses down on the pedal, it opens the throttle, allowing more air and fuel into the engine, which in turn propels the vehicle forward. However, the mechanics of this seemingly straightforward action involve a series of complex systems working in harmony.
Traditionally, the connection between the gas pedal and the throttle was managed through a physical cable. This cable would run from the pedal to the throttle body, translating the driver’s foot movement into a mechanical response. This system was incredibly effective for decades, providing a direct and tactile link between the driver and the car's power.
The cable mechanism offered drivers an immediate and predictable reaction. When the driver pushed the pedal, the cable pulled the throttle open, which often resulted in a gratifying acceleration experience. However, this system had its limitations, especially regarding efficiency and responsiveness. Variability in cable tension, wear over time, and the inability to easily integrate electronic control measures posed challenges that engineers needed to address.
The Shift to Electronic Throttle Control
With advancements in technology, many modern vehicles have transitioned from traditional cable-operated systems to more sophisticated electronic throttle control (ETC) systems. Instead of a mechanical cable, these systems utilize sensors, motors, and software to manage the car's throttle response.
cable gas pedal
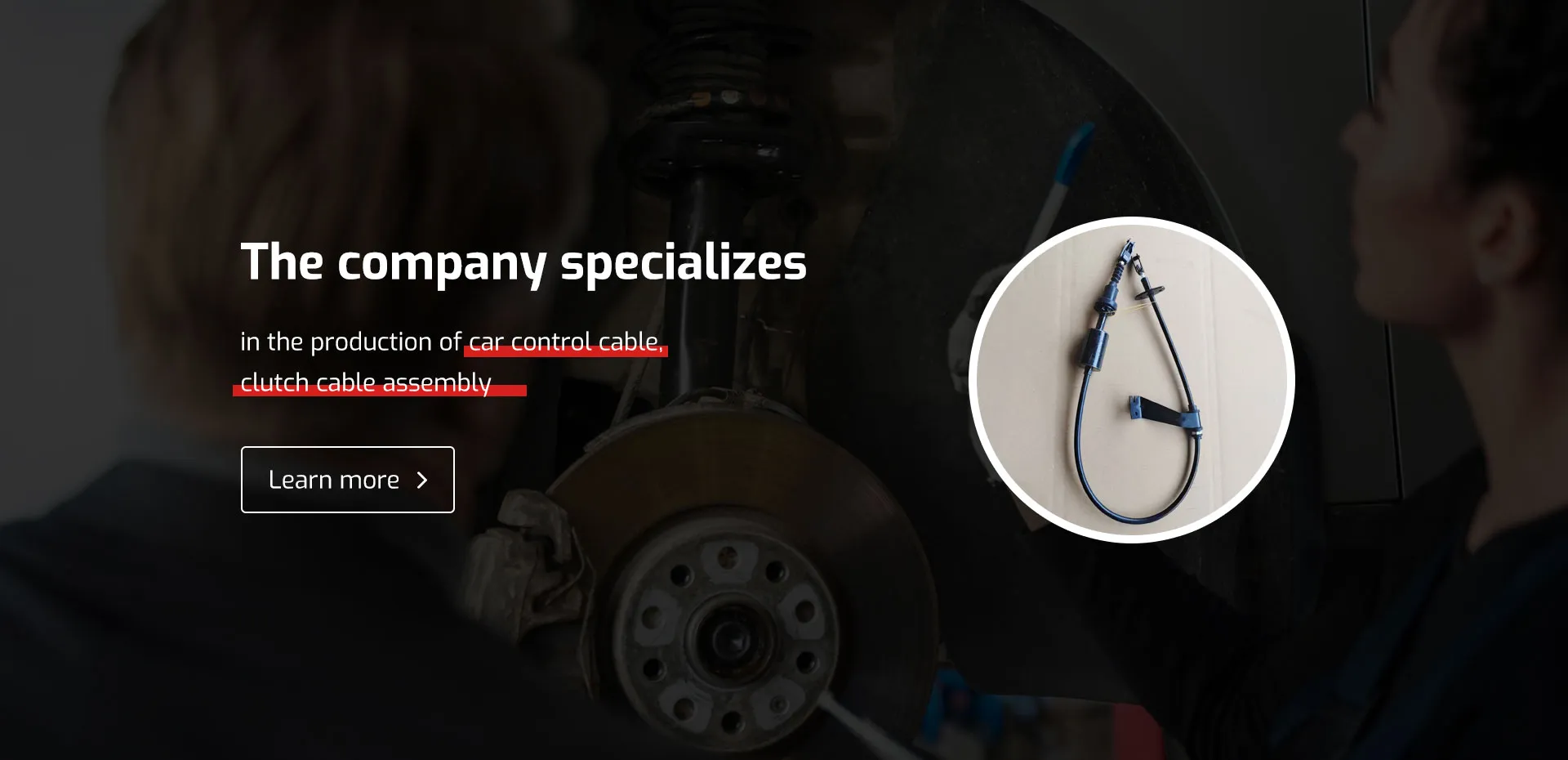
In an ETC system, the gas pedal operates as a sensor that sends electrical signals to the car's engine control unit (ECU). The ECU then calculates the appropriate throttle opening based on various inputs, including vehicle speed, engine load, and even traction conditions. This allows for a more nuanced response to driver inputs, enhancing performance while optimizing fuel efficiency.
The benefits of electronic systems are manifold. For one, they can adapt to different driving conditions, providing improved stability under various circumstances. Additionally, electronic controls enable the integration of advanced features like cruise control, traction control, and even autonomous driving technologies. As vehicles become smarter, the role of the pedal transforms from a simple actuation device to part of a broader array of sensors feeding information to the vehicle's brain.
Performance and Driving Experience
Ultimately, whether through a traditional cable system or a modern electronic setup, the interaction between the gas pedal and the engine has profound implications on the driving experience. Enthusiastic drivers often appreciate the tactile feedback of a cable-linked system, enjoying the direct communication between foot and engine. However, a significant number of consumers favor the smooth, seamless acceleration provided by electronic systems.
Car manufacturers continue to innovate in this area, exploring ways to enhance driver engagement and vehicle responsiveness. For instance, some luxury and performance cars incorporate feedback systems to simulate the feel of a cable throttle, providing both the comfort of modern technology and the emotional connection reminiscent of classic vehicles.
Conclusion
The interplay of the cable, gas, and pedal illustrates a fascinating evolution in automotive technology. From the straightforward yet effective cable systems of the past to the advanced electronic throttle controls of the present, the relationship between driver input and vehicle response has continually improved. As technology evolves, we can expect further innovations that will refine this interaction, ultimately leading to vehicles that not only respond with precision but also create a richer driving experience for users. Whether it's through the nostalgia of a physical cable or the futuristic promise of electronic systems, the gas pedal remains a key player in how we engage with our automobiles, embodying the spirit of innovation that drives the automotive industry forward.
-
Upgrade Your Control with Premium Throttle CablesNewsAug.08,2025
-
Stay in Control with Premium Hand Brake CablesNewsAug.08,2025
-
Experience Unmatched Performance with Our Clutch HosesNewsAug.08,2025
-
Ensure Safety and Reliability with Premium Handbrake CablesNewsAug.08,2025
-
Enhance Your Vehicle with High-Performance Clutch LinesNewsAug.08,2025
-
Elevate Your Ride with Premium Gear CablesNewsAug.08,2025
