dual cable throttle assembly
Understanding Dual Cable Throttle Assemblies
The dual cable throttle assembly is a crucial component in many vehicles, particularly those with traditional internal combustion engines. It plays a vital role in controlling the engine's throttle, thereby regulating the engine's power and speed. As vehicles continuously evolve, understanding the functionality and importance of this system becomes essential for both automotive enthusiasts and professionals.
At its core, the dual cable throttle assembly consists of two cables one for the throttle opening and the other for returning the throttle to its closed position. This design provides a mechanism for redundancy and safety. In the event of a failure in one of the cables, the other can still provide some level of control, reducing the risk of throttle sticking, which could potentially lead to dangerous situations on the road.
The primary function of the throttle assembly is to manage air intake into the engine. When the driver presses the accelerator pedal, the throttle cable pulls open the throttle plate, allowing more air to enter the engine. This increased airflow, paired with the appropriate amount of fuel, results in greater power output. Conversely, when the driver releases the pedal, the return cable ensures that the throttle plate closes, reducing airflow and consequently the engine's power.
dual cable throttle assembly
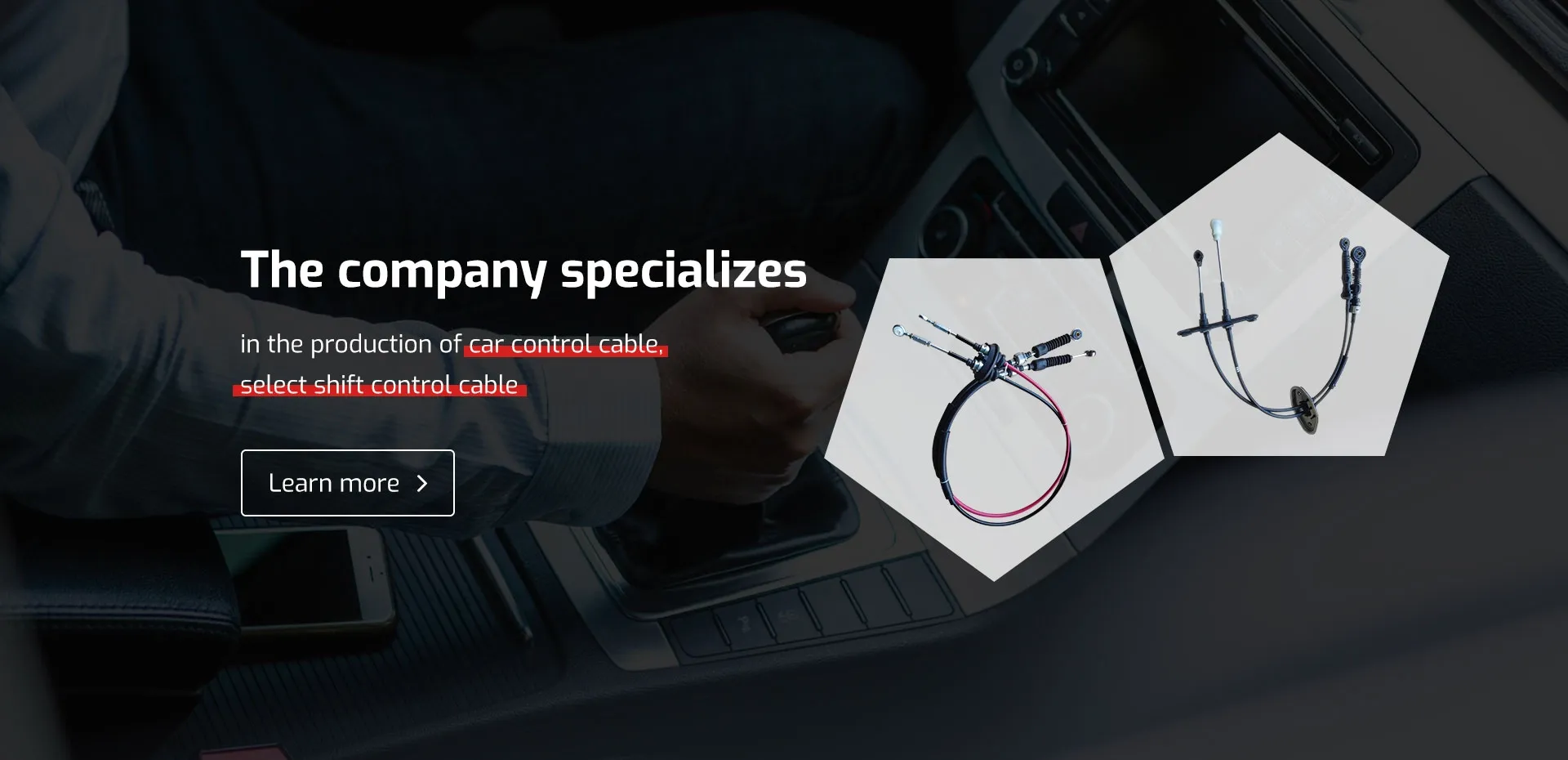
One of the most significant advantages of a dual cable system is its enhanced feel and responsiveness. Many drivers appreciate the direct connection between the pedal and the engine, offering immediate feedback and a more engaging driving experience. This responsiveness can be particularly noticeable in performance vehicles, where precision in throttle control can greatly enhance acceleration and overall driving dynamics.
Moreover, the dual cable throttle assembly is often more straightforward to repair and replace compared to modern electronic throttle control systems, which rely on sensors and electronic signals. Mechanics familiar with older systems can quickly diagnose and fix issues related to cable wear or tension without the need for specialized diagnostic equipment.
However, as automotive technology advances, many manufacturers are moving towards electronic throttle control (ETC) systems. These systems utilize sensors to detect the position of the accelerator pedal and send electronic signals to the engine control unit (ECU) to manage throttle position. While electronic systems provide precise control and can improve fuel efficiency and emissions, they lack the mechanical simplicity and reliability of dual cable assemblies.
In summary, the dual cable throttle assembly remains a significant component in many vehicles, representing a blend of mechanical simplicity and effective performance. While the industry trends towards more sophisticated electronic systems, there's a certain appeal and reliability in the dual cable design that continues to resonate with many drivers and automotive purists. For those maintaining older vehicles or seeking a more tactile driving experience, understanding the nuances of the dual cable throttle assembly can deepen their appreciation for automotive engineering and enhance their overall driving experience. Whether you're in a classic car or navigating modern streets, the connection between driver input and engine response remains at the heart of automotive performance.
-
Workings of Clutch Pipe and Hose SystemsNewsJun.04,2025
-
The Inner Workings of Hand Brake Cable SystemsNewsJun.04,2025
-
The Secrets of Throttle and Accelerator CablesNewsJun.04,2025
-
The Hidden Lifeline of Your Transmission Gear Shift CablesNewsJun.04,2025
-
Demystifying Gear Cables and Shift LinkagesNewsJun.04,2025
-
Decoding Clutch Line Systems A Comprehensive GuideNewsJun.04,2025
